JSER Policies
JSER Online
JSER Data
Frequency: quarterly
ISSN: 1409-6099 (Print)
ISSN: 1857-663X (Online)
Authors Info
- Read: 48811
|
НВ/ХН: МОЖНА ДИЈАГНОЗА И ТРЕТМАН
Карл РАЈХАЛТ 1
Оддел за педијатриско истражување, Универзитет во Осло, Rikшospitalet1 |
|
AD/HD: POSSIBLE DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT
Karl REICHELT 1
Department of Pediatric Research, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Вовед |
|
Introduction |
|
Медицинската дијагноза за НВ/ХН наголемо се засновува на клиничките знаци или на групата симптоми. Според ова честопати се вели дека на децата со аутизам може да им се даде дополнителна дијагноза за НВ/ХН. Ова е погрешно како резултат на хиперактивноста причинета од разликата во етиологијата. Заедничкиот именител при НВ/ХН е хипервозбудување на деловите кои се поврзани со ЦНС (Централниот нервен систем) и се назначени примерите. Децата со аутизам имаат профил на спротивно возбудување. Според ова тие покажуваат бавно адаптирање додека децата со НВ/ХН имаат брза адаптација. Според ова психолошките проблеми со вниманието се различни. Вообичаениот третман со лекови и различните интервенции во диетата се од особено значење. На крај ви ја презентираме нашата петгодишна интервенција во диетата проследена кај мала група пациенти со НБ/ХН. Можеме да заклучиме дека интервенцијата во диетата е најверојатно најбезбедна за разлика од третманот со лекови и соодветно на ова треба почесто да се применува. |
|
Medical diagnosis of AD/HD is largely based on clinical signs or symptom clusters. It is therefore often stated that for instance autistic children can have an additional diagnosis of AD/HD. This is false and due to hyperactivity caused by difference in aetiology. The common denominator in AD/HD is hypo-arousal in the attention related parts of the CNS (Central Nervous System) and examples are quoted. Autistic children have opposite arousal profiles. Thus they show slow habituation while AD/HD kids show fast habituation. Attention problems are therefore physiologically different. The usual drug treatment and various dietary interventions are outlined. Finally we present our five year dietary intervention follow up of a small group of AD/HD patients. We conclude that dietary intervention is probably safer than drug treatment and should be tried more extensively. |
|
|
|
|
|
Генетика |
|
Genetics |
|
НБ/ХН има особено силна генетска предиспозиција (1-4). Сепак, за да се прикажат генетските грешки на ензимите или останатите метабилитички активни протеини, мора да бидат преоптоварени со субстанциите кои се производ на метаболизмот, приближно до недостаток на ензими. Пример за ова е нару- |
|
AD/HD has a strong genetic disposition (1-4). However, to become manifest genetic defects of enzymes or other metabolically active proteins must be overloaded by metabolites proximal to the insufficient enzyme. An example of this is Følling’s disorder (phenylketonuria) where the amino acid phenylalanine (F) is not broken down in the liver. It consequently increases to toxic levels, and also opens up secondary pathways (just like a dam in river when it overflows). It is treated by throttling the input (removing F from diet) to the extent that only sufficient amounts of F are ingested to synthesise important transmitters. If some rest activity of the critical enzyme is present co-factor increase can restore some activity (change the Km of the enzyme in vivo) (5) and also by mass –action. |
|
|
|
|
|
Дијагноза |
|
Diagnosis |
|
НВ/ХН како и останaтите медицински дијагнози, пред сè е заснован на симптомите, набљудуваниот феномен како што е споменат и опишан во DSM IV или ICD 10. Ова би значело дека групите на симптоми се земаат предвид при прикажувањето на болеста, но ова не е вообичаено и повеќето дијагнози имаат свои подгрупи со оглед на фактот што симптомите не кажуваат ништо за етиологијата. |
|
AD/HD is, as many medical diagnoses, based mainly on symptoms, observed phenomena as listed and described in DSM IV or ICD 10. This means in short that clusters of symptoms are taken to represent a disease entity, but this is usually not so, and most diagnoses contain subgroups since symptoms do not tell anything about aetiology. |
|
|
|
|
|
Патопсихолошкадијагноза |
|
Patho-physiologic diagnosis |
|
Основа во физиологијата е слабото спроведување на кожата на дланките на рацете, со брза адаптација и слаба реакција на сензорните дразби (ова е спротивно кај децата со аутизам) (6,7). Ова ја потврдува општата физиологија којашто покажува дека зголеменото задржување кај ЦНС (Централниот нервен систем) што ја причинува хиперактивноста и проблемите со вниманието (11-13). Според недостатокот на рецепторот на тироидниот хормон во ЦНС (13) би создале намалување на активирањето. Ова типично се прикажува преку лекарствата против епилепсија кои што го зголемуваат ова инхибирање при дразнењето на соодевтните делови на ЦНС и го причинува соодветното однесување. |
|
Central to the physiology is low skin conductance in the palms of the hands, with fast habituation and low responses to sensory inputs (this is the opposite of autistic children) (6, 7). This confirms the general physiology which shows that increased inhibitory tone in the CNS (Central nervous system) causes hyperactivity and attention problems (11-13). Thus thyroid hormone receptor deficiency in the CNS (13) would cause decreased activation. This is typically demonstrated by antiepileptic drugs that increase this inhibition in arousal related parts of the CNS and causes acting out behaviour. |
|
|
|
|
|
Третман |
|
Treatment |
|
A. Лекови
Б. Интервенции во исхраната
В. Додатоци во исхраната
Г. Останати фактори |
|
A. Drugs:
B: Dietary interventions:
C: Food additives:
D. Other factors: |
|
|
|
|
|
Какоеовафизиолошкиможно |
|
How is this physiologically possible and probable? |
|
Пептидите кај животните се формираат во цревата на животните (52) и кај луѓето (53, 54). Протеините особено целите се преземаат (55) како пептиди (56). Иако протеините кои се внесени од страна на мајката може да се вратат преку мајчиното млеко (57-60). Зголеменото внесување од внатрешноста се среќава кај животните кога релевантните пептидизи се инхибирани (61). Драматичен е примерот на отровот ботулиниум којшто е пептидизарен ензим и којшто може да се внесе од внатрешноста, да ја премине бариерата крв - мозок и да прекине една пептидна врска кај протеинот СНАП-25 од што може и да настапи смрт (62). Понатаму опиодните пептиди од случајот со млекото, ја поминуваат бариерата крв - мозок и има длабински ефекти врз животните (63,64) и кај човекот (65). |
|
Peptides are formed in the gut in animals (52) and in man (53, 54). Proteins also intact ones are taken up (55) as are peptides (56). Thus proteins ingested by mothers can be recovered from mothers’ milk (57-60). Increased uptake from the gut is also found in animals when the relevant peptidase is inhibited (61). A dramatic example is Botulinum toxin which is a peptidase enzyme that can be taken up from the gut, passes the blood –brain “barrier “ and cuts one peptide bond in the protein SNAP -25, from which we may die (62). Furthermore peptides from casein in milk cross the blood –brain barrier and have profound effects in animals (63,64) and man (65). |
|
|
|
|
|
Дасеспречипогрешнатаисхранасодиета |
|
To prevent malnutrition on diet |
|
Како дополнување користиме витамин Ц 250 мг, калциум 500 мг и мултивитамини (мулти) дневно. 1-3 пати неделно треба да се внесе N-acetyl-cystein со цел да се зголеми интраклеточниот глутатион (GSH) за врзување на тешките метали и има антиоксадитивен ефект. |
|
In addition cod liver oil, we use Vitamin C 250 mg, Calcium 500 mg and Multivitamins (Multi) daily. 1-3 times weekly N-acetyl-Cystein should probably be supplied to increase intracellular glutathione (GSH) for heavy metal chelating and anti oxidative efficiency is useful. |
|
|
|
|
|
Прелиминарниподатоциод 5-годишното следење на случајот за слободна интервенција кај НВ/ХН |
|
Preliminary data from a 5 year |
|
По анализата на урината за профилот на пептидите, децата со симптоми на НВ/ХН опишани според DSM IV се ставаат на слободна диета. Се следат повеќе од пет години за да се неутрализира кој било плацебо-ефект. На сликте 1 и 2 е прикажана петгодишната промена од почетокот на оцените во CBCL и намалувањето на пептидите во урината. Ова е во насока на очекуваното. |
|
After urine analysis of peptide profiles, kids with the characteristic symptoms of AD/HD, described in DSM IV, were put on a casein free diet. They have been followed for more than 5 years to counteract any placebo effects. In figures 1 and 2 the 5 year change from start in CBCL scores and peptide decrease in urine is shown. This is clearly in line with expectation. |
|
|
|
|
|
Заклучок |
|
Conclusion |
|
Не постои причина да не се проба со диета за НВ/ХН. Поголемиот дел од човештвото не користи млеко по 16-годишна возраст и повеќето користат ориз отколку житарици. Диетата е без вистински опасности и покажува значително ветување во повеќето објавени и внимателно разгледани трудови. Дијагнозата би требало да ги вклучи TSH, T4 и T3 (13). Треба да се истражи дали е можна спроводливост и привикнување на кожата на пептидите од урината и IgA-антителата од протеините во храната измерени во серум (21). |
|
There is no reason not to try diet in AD/HD. The larger part of mankind does not use milk after the age of 6, and most live on rice rather than grains. Diet is without real dangers and shows great promise in most published and peer reviewed papers. The diagnosis should probably include TSH, T4 and T3 (13). If possible skin conductance and habituation, urine peptides and IgA antibodies to food proteins measured in serum should be investigated (21). Diet and removal of certain food additives is efficient and safe treatment of AD/HD. The diet must be strict. Alternatives are: |
|
|
|
|
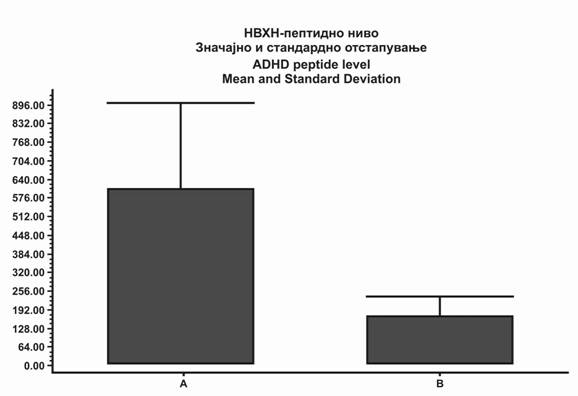
|
Слика 1. Прелиминарни резултати кои се добиени по пет години од примената на диетата по отстранувањето на целиот пептиден материјал по измивањето со хипуричната киселина. Нивото на почетокот и она по пет години се разликуваат со p = 0.018 и Wilcoxon-тестот на паровите е поврзан. А: пред почетокот на диетата. Б: по пет години. Средината е областа под кривината од 215 нм. измиена со хипуричната киселина. |
|
Fig. 1. Preliminary result obtained after five years of diet on total peptide like material eluting after hippuric acid. Initial and 5 year levels are different with p = 0.018 Wilcoxon paired test, two tailed. A: before start of diet. B. After five years. Ordinate is area under the 215nm curve, eluting after hippuric acid. |
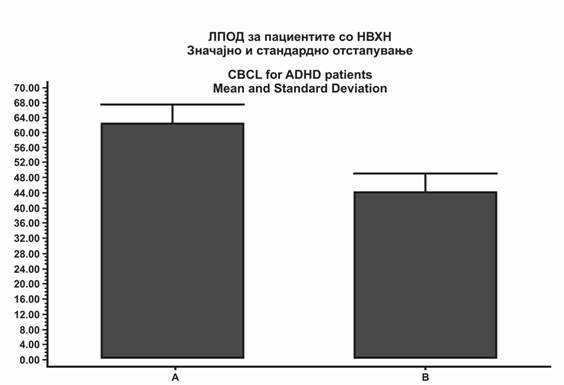
|
Слика 2. Листа за проверка на однесувањето на детето (ЛПОД) пред и по 5 години од диетата. P =0.012 и Wilcoxon-тестот на паровите е поврзан. А е почетната оцена и Б оцена по пет години. Средина се оцените за ЛПОД за децата без проблеми има средна вредност од 50 (SD 10). |
|
Fig. 2. Child behavior check list (CBCL) before and after 5 years on diet. P =0.012, two tailed Wilcoxon paired test. A is start score and B after 5 years. Ordinate is CBCL scores which for children without problems has a mean of 50 (SD 10). |
|
Citation:Reichelt K, Nodland M, Fosse K, Knivsberg AM. AD/HD: Possible Diagnosis and Treatment. J Spec Educ Rehab 2008; 9(3-4):85-95. |
||||
|
|
||||
|
Литература / References |
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
Share Us
Journal metrics
-
 SNIP 0.059
SNIP 0.059 -
 IPP 0.07
IPP 0.07 -
 SJR 0.13
SJR 0.13 -
 h5-index 7
h5-index 7 -
 Google-based impact factor: 0.68
Google-based impact factor: 0.68
10 Most Read Articles
- PARENTAL ACCEPTANCE / REJECTION AND EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE AMONG ADOLESCENTS WITH AND WITHOUT DELINQUENT BEHAVIOR
- RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN LIFE BUILDING SKILLS AND SOCIAL ADJUSTMENT OF STUDENTS WITH HEARING IMPAIRMENT: IMPLICATIONS FOR COUNSELING
- EXPERIENCES FROM THE EDUCATIONAL SYSTEM – NARRATIVES OF PARENTS WITH CHILDREN WITH DISABILITIES IN CROATIA
- INOVATIONS IN THERAPY OF AUTISM
- AUTISM AND TUBEROUS SCLEROSIS
- DIAGNOSTIC AND TREATMENT OPTIONS IN AUTISTIC SPECTRUM DISORDERS – AN OVERVIEW
- THE DURATION AND PHASES OF QUALITATIVE RESEARCH
- REHABILITATION OF PERSONS WITH CEREBRAL PALSY
- DISORDERED ATTENTION AS NEUROPSYCHOLOGICAL COGNITIVE DISFUNCTION
- HYPERACTIVE CHILD`S DISTURBED ATTENTION AS THE MOST COMMON CAUSE FOR LIGHT FORMS OF MENTAL DEFICIENCY
















