JSER Policies
JSER Online
JSER Data
Frequency: quarterly
ISSN: 1409-6099 (Print)
ISSN: 1857-663X (Online)
Authors Info
- Read: 42223
|
ПРИСУСТВО НА АДЕНОИДНИ ВЕГЕТАЦИИ НАЗАЛЕН ГОВОР И НАМАЛУВАЊЕ НА СЛУХОТ ВО РЕЛАЦИЈА СО СЕКРЕТОРЕН ОТИТИС МЕДИА ВО ДЕТСКАТА ВОЗРАСТ
Габриела КОПАЧЕВА, Марина ЧАКАР, |
|
THE PRESENCE OF ADENOID VEGETATIONS AND NASAL SPEECH, AND HEARING LOSS IN RELATION TO SECRETORY OTITIS MEDIA
Gabriela KOPACHEVA, Marina CHAKAR, |
|
Вовед |
|
Introduction |
|
Секреторниот отитис медиа (СОМ), најчесто се јавува во детската возраст, најчесто кај предучилишните и училишните деца. СОМ представува насобирање на течност во средното уво без знаци и симптоми за акутна инфламација. Се смета дека важен фактор во етиопатогенезата на СОМ претставува дисфункција на Евстахиевата туба аудитива. |
|
Secretory otitis media (SOM) is one of the most common childhood concerns mainly in preschool and school children. SOM is a collection of fluid in the tympanic cavity without the signs and symptoms of acute inflammation. Abnormal Eustachian tube function appears to be the most important factor in the pathogenesis of SOM. Children with SOM typically have rather elevated, fluctuating hearing thresholds of about 20-25 dB (1, 6). They complain of ear fullness or tinnitus (1, 3). |
|
|
|
|
|
Материјал и методи |
|
Material and Methods |
|
Клиничкото иследување беше спроведено кај 68 деца, на возраст од 3-17, кои беа поделени во две групи, врз база на резултатите добиени при дигитална палпација на епифаринкс и фиберепифаронгоскопија. |
|
Subjects of the clinical investigation were a group of 68 children at the age of 3-17. Accordingly to the clinical examination (digital assessment and nasofiberscope) children were divided into 2 groups. |
|
Кај децата од првата група беа поставени вентилациони цевчиња, а кај децата од втората група покрај вентилациони цевчиња беше направено и аденоидектомија. Тонално аудиометриско испитување и тимпанометрија беше направена пред и по операцијата со помош на аудиолошка апаратура (аудиометер-Hortman CA 540) и клинички тимпанометар (Hortman тип 87). Не постоеше сигнификантна разлика во χ2-тестот меѓу сите групи (p>0,05) (Слика 1). |
|
Ventilation tubes were inserted in children from the first group, and the children from the second group underwent adenoidectomy and ventilation tube insertion. The pure tone audiometry and tympanometry were performed pre and postoperatively using audiological equipment (Audiometer Hortman CA 540) and clinical tympanometer (Hortman type 87). There was not a significant difference in χ2-test between the groups (p>0.05) (Fig. 1.). |
|
|
|
|
|
Резултати |
|
Results |
|
Резултатите се изразени како просечни вредности во разликата помеѓу коскената и воздушната спроводливост пред и по хируршкиот третман. Не се докажа сигнификантна разлика меѓу децата со СОМ со или без хипертрофични аденоиди. Тимпанометриските тестови покажаа дека фрекфенцијата на афекцијата на едното или двете уши е слична во двете групи. Евалуацијата на резултатите од спроводниот третман се базираше на промените кои беа регистрирани на тимпанограмот (5). |
|
The treatment results were expressed as an average air bone conduction pure tone, and air-bone gap difference in pre and post surgical procedure. No significant difference was shown between children with SOM with or without hypertrophic adenoids. |

|
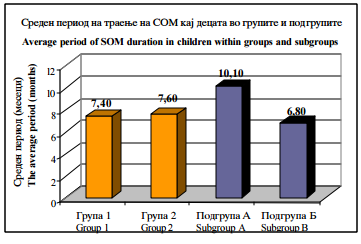
Слика 1. Среден период на траење на СОМ кај децата поделени во групи и подгрупи |
|
Figure 1. Average period of SOM duration in children in groups and subgroups |
   |
||
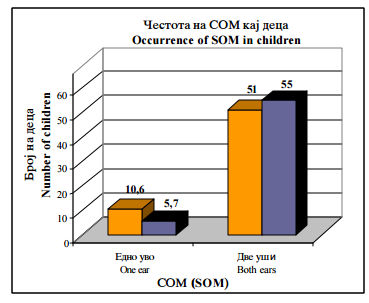
| Слика 2. Честота на појава на СОМ кај децата (χ²=1,62 p=0,02) |
|
Figure 2 Occurrence of SOM in children |
|
|
||
|
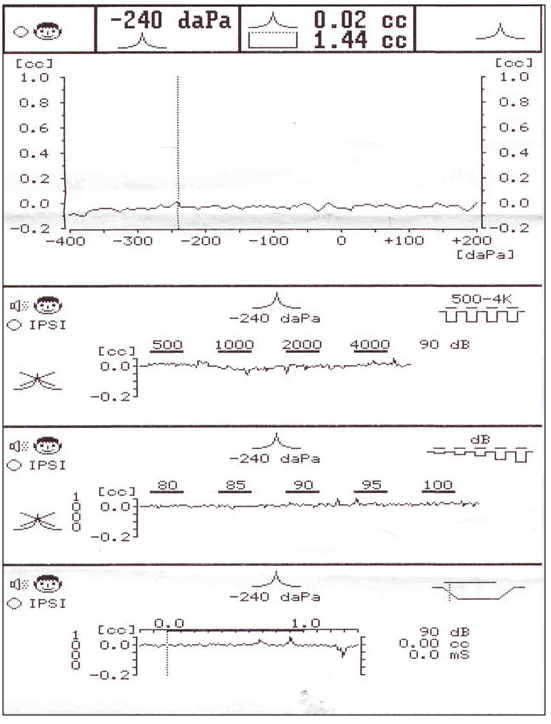
Слика 3. Тимпанограм тип Б. Кондуктивно намалување на слухот |
|
Figure 3. Tympanogram type B. Conductive hearing loss. |
|
Дискусија |
|
Discussion |
||
|
Многу клиничари сметаат дека хипертрофичните аденоиди имаат влијание во патогенезата на СОМ, а други пак не се согласуваат со оваа теорија. Недостатокот на заедничката методологија, различните методи на селекција, може делумно да ги објаснат овие различни ставови. Резултатите укажуваат дека нема директна врска меѓу големината на аденоидите и текот на СОМ. Кај децата од втората група имаше побрзо подобрување на слухот по хируршкиот третман во однос на децата од првата група (6, 7). |
|
Many clinicians emphasize the great influence of enlarged adenoid on SOM occurrence. Some investigators do not agree with this theory. Lack of agreement over methodology, different selection methods can partially explain these different opinions. |
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
Citation:Kopacheva G, Chakar M, Dubrovska L. The Presence of Adenoid Vegetations and Nasal Speech, and Hearing Loss in Relation to Secretory Otitis Media. J Spec Educ Rehab 2004; 5(3-4):57-62. |
||||
|
|
||||
|
Литература / References |
|
|
||
|
1. Antenius L J C, Engel J A, Hendiks J J, T.jr Hendriks J J T, Marres EH. Otitis media with effusion algorithms and aassociated hearing loss in infants 0-2 year. II European Conference of Audiology. Noordwijkerhout, Netherlands, 1995. |
|
5. Kazanas S, G Maw R. Tympanometry, stapedius reflex and hearing impairment in children with otitis media effusion. Acta Otolaryng, (Stockh.), 1994, 114, 410. |
||
Share Us
Journal metrics
-
 SNIP 0.059
SNIP 0.059 -
 IPP 0.07
IPP 0.07 -
 SJR 0.13
SJR 0.13 -
 h5-index 7
h5-index 7 -
 Google-based impact factor: 0.68
Google-based impact factor: 0.68
10 Most Read Articles
- PARENTAL ACCEPTANCE / REJECTION AND EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE AMONG ADOLESCENTS WITH AND WITHOUT DELINQUENT BEHAVIOR
- RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN LIFE BUILDING SKILLS AND SOCIAL ADJUSTMENT OF STUDENTS WITH HEARING IMPAIRMENT: IMPLICATIONS FOR COUNSELING
- EXPERIENCES FROM THE EDUCATIONAL SYSTEM – NARRATIVES OF PARENTS WITH CHILDREN WITH DISABILITIES IN CROATIA
- INOVATIONS IN THERAPY OF AUTISM
- AUTISM AND TUBEROUS SCLEROSIS
- DIAGNOSTIC AND TREATMENT OPTIONS IN AUTISTIC SPECTRUM DISORDERS – AN OVERVIEW
- THE DURATION AND PHASES OF QUALITATIVE RESEARCH
- REHABILITATION OF PERSONS WITH CEREBRAL PALSY
- DISORDERED ATTENTION AS NEUROPSYCHOLOGICAL COGNITIVE DISFUNCTION
- HYPERACTIVE CHILD`S DISTURBED ATTENTION AS THE MOST COMMON CAUSE FOR LIGHT FORMS OF MENTAL DEFICIENCY